Mate was never so consumed worldwide and the beverage is already exported to over 120 countries, among them, China and India, big tea consumers and producers.
Who said that mate is mate is right. According to the most respected tea sommelier in Brazil, Carla Saueressig, mate is not tea, because it doesn’t come from camellia sinensis, or assamica. It is an infusion because everything that is not from camellia sinensis ends up by being an infusion. However, for her, this is a very simplistic explanation. She reminds that, in Portugal, caffeine-free herb infusion is called tisane, to drink at night. But that is not the case of yerba mate, because it contains caffeine. “I bet on mate or “mate tea”, a name that is already institutionalized in Brazil. My friend Luiz Horta, one of the most respected journalists, specialized in wine and gastronomy, also says that he will die using the denomination mate tea”, says Carla.
Rio Grande do Sul producers are revolutionizing the ways of growing yerba mate and its commercialization
Yerba mate comes from an Atlantic Forest tree, Ilex Paraguariensis, which can reach up to 15 meters in height. It occurs in the country’s south states of Paraná, Santa Catarina and in the south of Mato Grosso do Sul, and is present in 3% of the whole Brazilian territory, corresponding to 450 square km. It is also found in Argentina and Paraguay, while Uruguay is the largest world consumer.
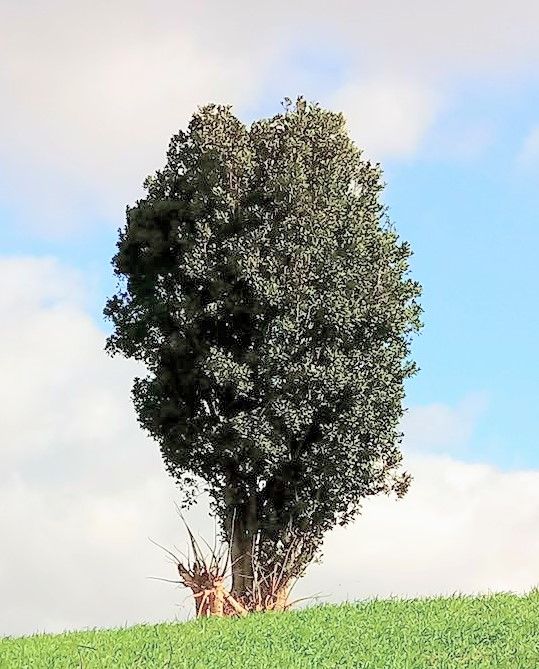

Example of Ilex Paraguarienses.
In Ilópolis municipality, in Rio Grande do Sul, around 800 small rural farmers, descending from Italian immigrants, are working on an authentic revolution in the method of growing and trading yerba mate.
Led by Inovamate, from Rio de Janeiro geographer Ariana Maia and her husband Clóvis Maia – third generation of yerba mate producers -, the new method used to produce yerba mate includes new cares during plantation, after harvest, in the training of mateiros (workers in yerba mate cultivation), and, mainly, in the partnership with several universities to conduct research for development of new products and new forms of consumption, much beyond chimarrão and tereré preparation.
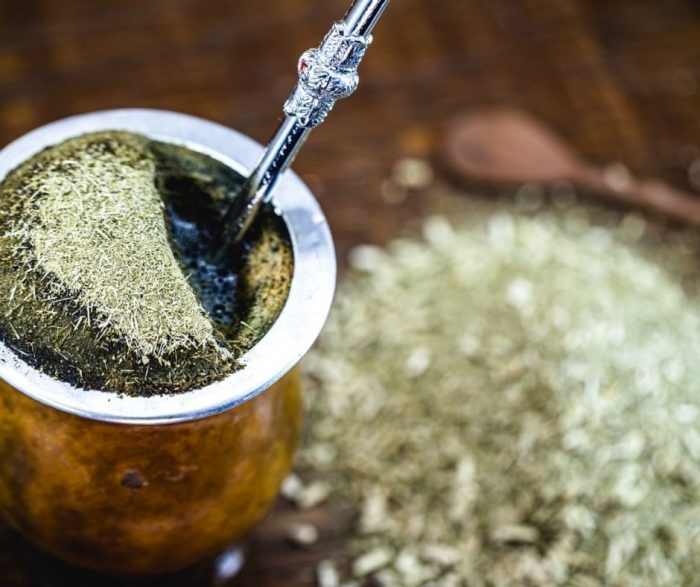
Yerba mate in cup
“Our main goal with Ilópolis producers’ community is to increase yerba mate consumption in the domestic market, in regions other than the South, betting on the use of the green yerba mate in a cup, like a tea, mixed with ingredients from other regions of the country. And also as a new ingredient in culinary, as powder, similar to the Japanese matchá, to be added in recipes of cakes, breads, puddings, jellies, honey, pasta, pizza dough, juice, farofa (prepared with manioc flour). An innovation that the best chefs in the country are already adopting. Imagination is the limit”, explains Ariana.
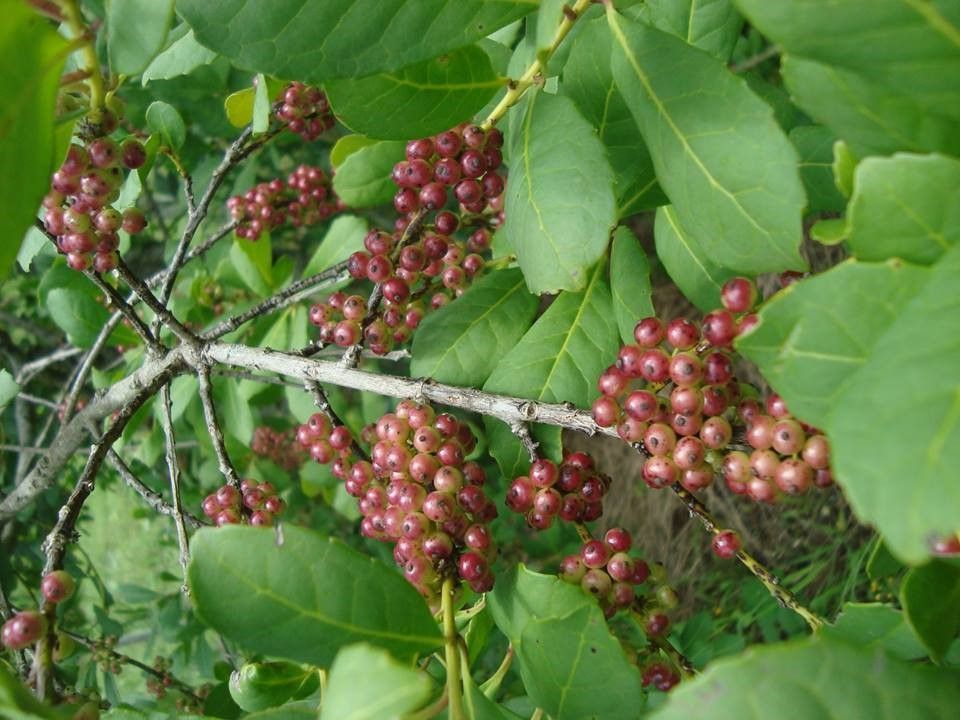

Yerba mate fruits will be used in the manufacture of cachaça.
Another novelty that promises to surprise the market is the launching of yerba mate cachaça (brandy), product developed thanks to Federal University of Rio Grande do Sul research. “Producers bet that yerba mate can follow the same path as that of coffee, with production of microlots with different terroirs and characteristics. We observed the special coffee and wine markets to learn”, she adds.
Each of these 800 small farms in Ilópolis region has around 15 to 17 hectares and 85% of them have yerba mate as main activity. Other activities are pig farming, milk, citrus and tobacco. “We are talking about eight to nine million yerba mate trees planted that, a short while ago, did not count on appropriate management, which did not enable traceability, and plants around it wouldn’t receive proper attention. That goes without mentioning that consumption in other uses was not considered”, tells Ariana.
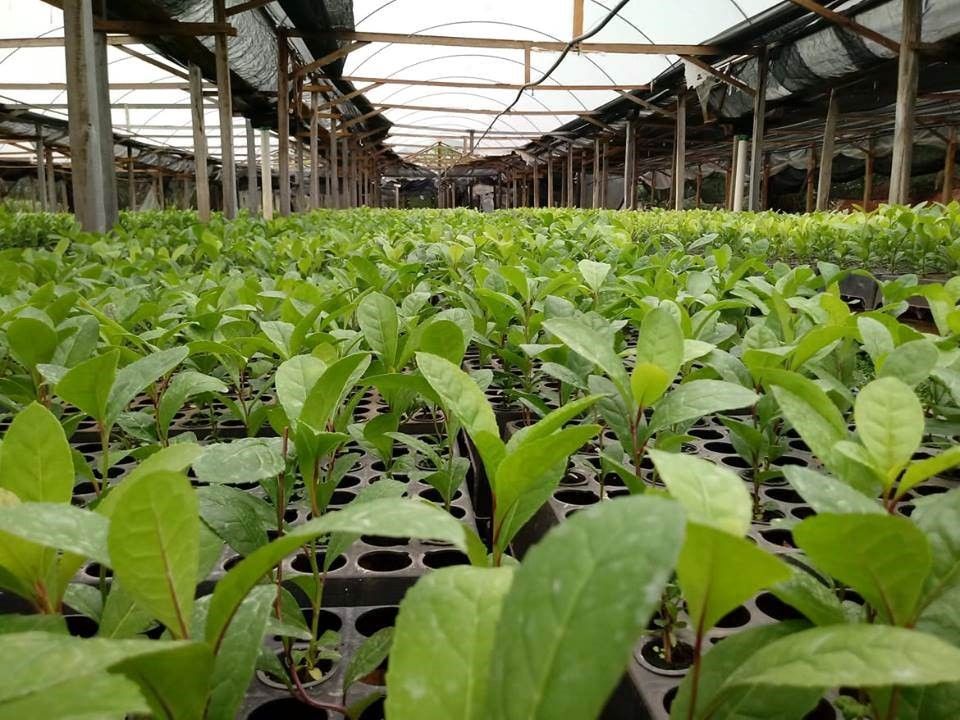

Yerba mate management is a powerful tool to preserve the Atlantic Forest, where the plant is endemic.
Since the farms are in Atlantic Forest region, all owners must reserve a portion of the area for preservation. “Most of them are located in steep areas, with low productivity”, adds Ariana.

While coffee cultivation grew and became sophisticate, yerba mate cultivation, for a long time, remained the same, essentially extractive. “For 40 years, we did not have public policies to the sector. There was the creation of the National Mate Institute, by Getúlio Vargas, in Rio de Janeiro, more due to a need, since Brazil exported yerba mate to Argentina, but Argentina became self-sufficient, which led to the creation of the institute, which lasted 20 years, from 1938 to 1958. Then, after its extinction, there were no public policies, which were only retaken in 2013 with the creation of the Brazilian Erva-Mate Institute, an initiative of Rio Grande do Sul state.
Legenda: While Brazilians use yerba mate to prepare chimarrão, with hot water, Paraguay people use it to prepare tereré, with cold water.
Yerba mate in microlots
In Maia family property, they are already getting prepared for, in the coming year, starting erva-mate sales in microlots, with controlled origin, as happens with special coffees. “Only in Rio Grande do Sul there are 58 species of Ilex Paraguaienses in the Germplasm Bank, and the continuation of research will provide countless flavors of yerba mate. Our first yerba mate microlot will be Reserva Roman, to be traded in small bags of 300 to 400 g. I think that, within five years, the whole sector will be offering its microlots to the market, with great flavor diversity. And we are working to offer different roasting process options, with different grain size, for yerba mate consumption both in cup and gourd”, says Ariana.
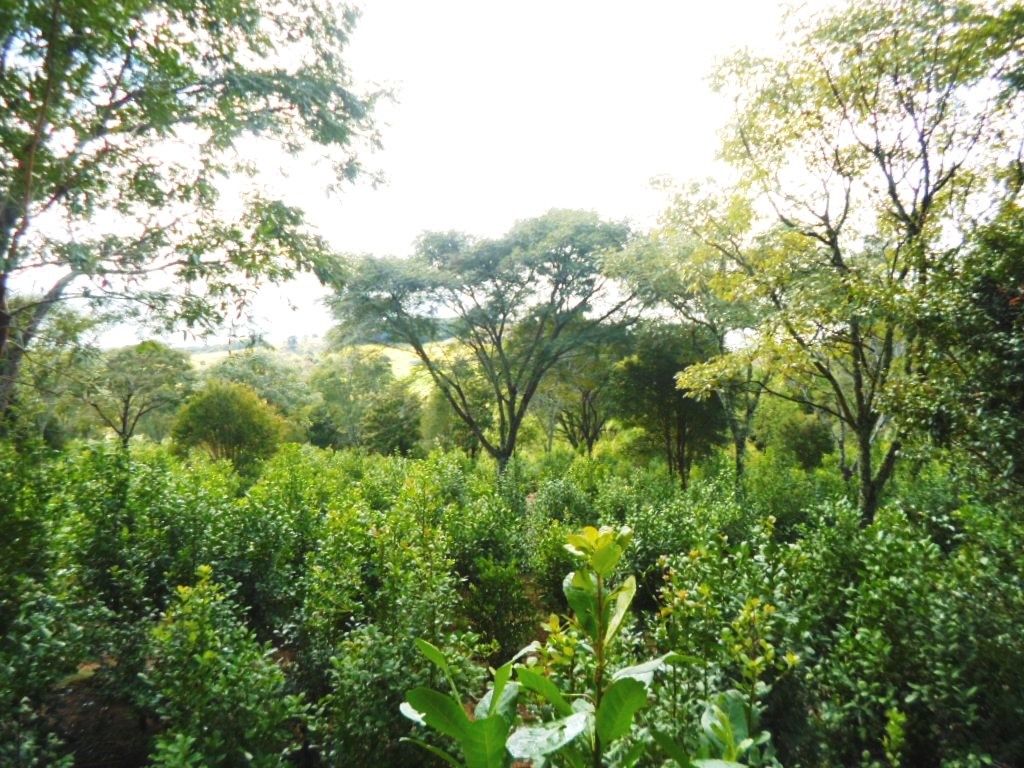

In Ilópolis, yerba mate is planted at altitude between 500 and 1,500 meter.
Yerba mate cultivation is made in agroforestry system, where the plant grows under the shadow of araucarias, mainly, one of the most threatened species of the Atlantic Forest.
For the technical coordinator of EMATER yerba mate quality valorization program Ilvando Barreto de Melo, who works for 26 years with yerba mate, this is the best moment to work on the cultivation. “Yerba mate is already being consumed in 120 countries and there is a strong process of valorization of the product, which caused a significant improvement in its quality and in good production practices”, he informs.
Brazil exports to 33 countries, while Argentina is the largest exporter, including to Syria, which introduced yerba mate in different markets. “This re-exportation is helping a lot in the process of expanding yerba mate consumption area worldwide, and today it can be found in Chile, Germany, USA, Canada, Japan, China and India”, he adds.
Rio Grande do Sul alone counts on 260 processing industries and, among them, 133 were already qualified to work with more strict norms and 165 professionals trained to work in the yerba mate sector, observing more strict rules of hygiene, with a protected harvest.
The researcher explains that Rio Grande do Sul has five yerba mate producer regions, comprising 206 municipalities with different terroirs and characteristics: Missões/Celeiro, with seat in Palmeira das Missões, yerba mate birth place, Alto Uruguai, in Erechim region, Rio Grande do Sul Northeast Region, Machadinho, Alto Taguari (Ilópolis) and Região dos Veles, with seat in Venâncio Aires, known as national capital of Chimarrão. “The importance of data analysis to plan strategies and organize the production system, considering regional characteristics and potentials, is essential for the yerba mate project success”, he says.
He explains that there are three different species of ilex paraguariensis: the one with purple stem, stronger, the one with white stem, and periquita, with a differentiated flavor.
According to Ilvandro, yerba mate consumption has grown significantly and Brazil has exported around 35 thousand tons a year. Eight years ago this number was 27 thousand tons, but to the end of 2020 and beginning of 2021 the expectation is the exportation of 40 thousand tons.
Those who want to visit yerba mate production, a good opportunity is to do so along with a specialist like Carla Saueressig, who organizes, since last year, the yerba mate Caravan, with visits to small farmers, industries and small artisans. For further information on dates and prices, send email to alojadochatg@gmail.com.
Yerba mate production processes